Back-to-School Concussion Information
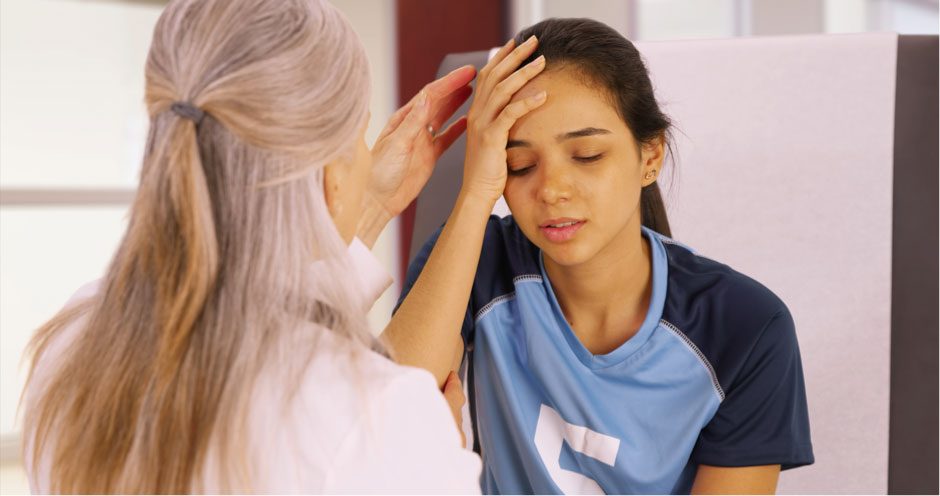

It’s that time of the year! With fall sports and pre-season practices just around the corner, it’s important that parents, children, and schools are armed with safety precautions and tips to avoid sports injuries.
It’s normal for us to hear about tragic stories of professional athletes who suffer from head injuries due to contact sports. The sad news is, not all sports-related injuries are exclusive to professional athletes. Sports injuries can happen to anyone, including children who play in school.
According to a Neurosurgery Journal, there are more than 500,000 emergency room visits yearly due to brain injuries among children ages 1-17. A head injury can be something as simple as a bruise or bump to something serious as a fracture in the skull. One of the most typical sports injuries are concussions. This is a serious risk to young athletes, so Physicians Premier, your ER in Corpus Christi prepared some useful information about concussions to parents.
What is a concussion?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines a concussion as a “type of traumatic brain injury – or TBI – caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or by a hit to the body that causes the head and brain to move rapidly back and forth.” This sudden movement creates chemical changes in the brain which at times, damages the brain cells.
Parents, young athletes, and the school authorities should watch out for:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Sensitivity to light
- Dizziness
- Sensitivity to noise
- Blurry vision
- Memory or concentration problems
- Feeling hazy, sluggish, groggy, or foggy
- Confusion
Parents should also note that the symptoms mentioned above could manifest hours after the incident. If your child has any of the symptoms above, it is very likely that they suffered from a concussion, and is in need of immediate medical care.
When should you go to the emergency room?
Not all head injuries warrant a trip to the emergency room. However, it is best that you bring your child for medical evaluation in the following cases:
- Feels nauseated or is vomiting
- The injured area won’t stop bleeding
- Has problems remembering things
- Has lost consciousness or is disoriented or confused
- Has a seizure
- Has trouble walking or keeping his balance
If your child shows any of the following symptoms, take him to your ER in Corpus Christi right away:
- Shows unusual behavior, have problems concentrating, or experiences mood swings
- Has a headache that won’t go away
- Feeling dizzy, numb, or weak
- Has a slur in his speech
- Has difficulty moving his eyes or has changes in his eyesight
- Has problems waking up or falling asleep